Here
ε
0
= 8
,
85
∙
10
−
12
;
ε
∞
is high-frequency dielectric permittivity;
ω
l
and
ω
0
are zero and pole of dielectric function
ε
(
ω
)
.
For longitudinal electromagnetic waves (
E
k
k
) from relationship (3) it
follows that
ε
(
ω
) =
ε
(
ω
l
) = 0
, i.e. frequency of longitudinal electromagnetic
waves for the material medium in question
ω
=
ω
l
=
const.
Usually it is assumed that in vacuum
ε
(
ω
) = 1
. According to formula
(3) it means that only the transverse waves are present. However, according
to the Maxwell equation div
~D
=
iε
0
ε
(
~k ~E
) = 0
transverse waves are
present in vacuum when
ε
= 0
.
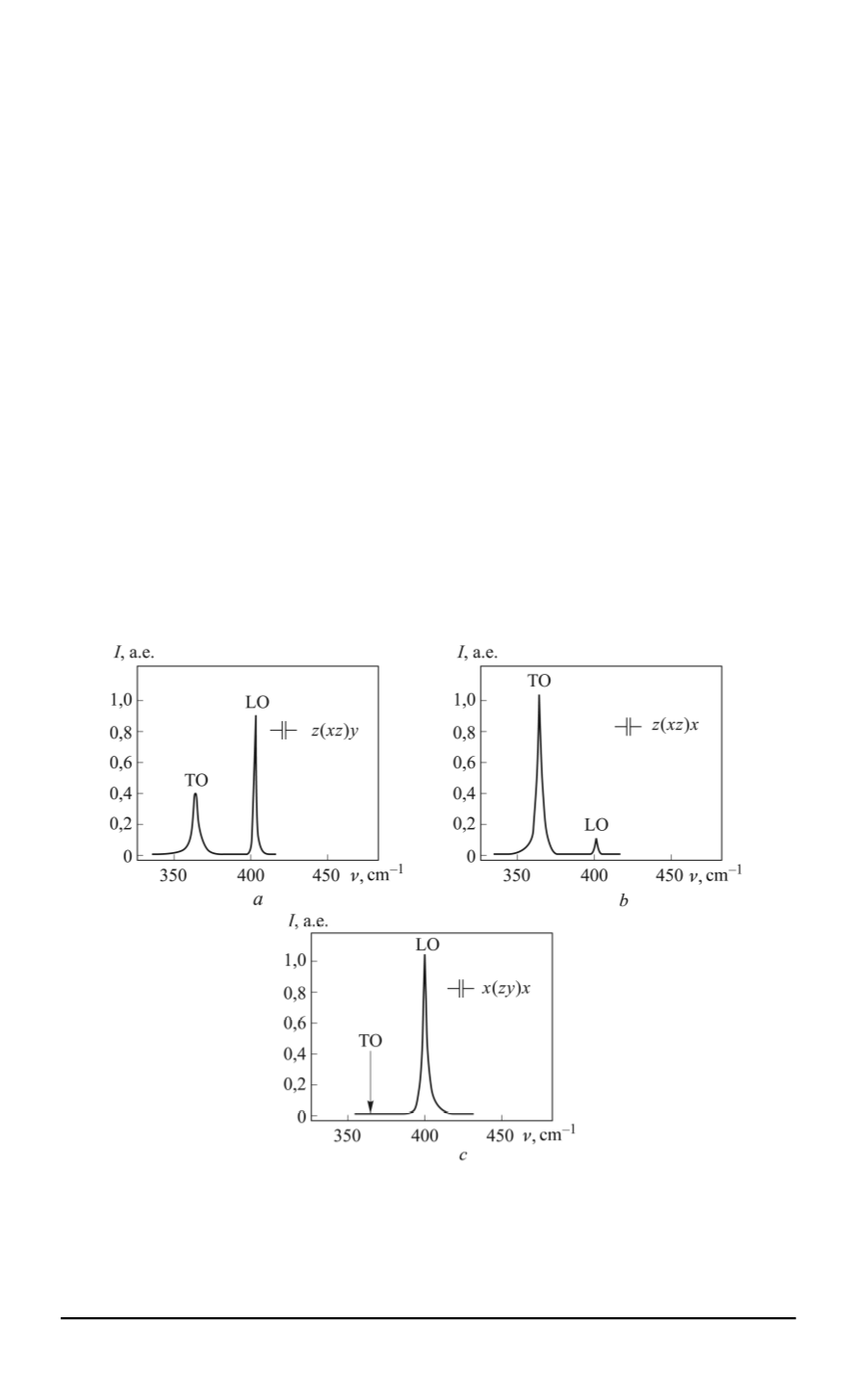
Polariton waves spectrum can be analyzed experimentally by the
spontaneous Raman scattering method. By selecting scattering geometry
and polarization installations transverse (TO) and longitudinal (LO) polar
modes can be detected. Spectra for TO and LO phonons at certain
polarization geometries in gallium phosphide monocrystal with planes
(100), (010) and (001) are presented in Fig. 1 [5]. Small-angle Raman
scattering for a gallium phosphide sample with a plane (111) perpendicular
to the the propagation direction of the exciting radiation ray allows
calculating frequencies of the lower branch polaritons and plotting a
dispersion curve piece in that crystal. So Raman scattering method in
Fig. 1. Spectra of Raman scattering by longitudinal and transverse polar modes
in a gallium phosphide crystal at scattering geometry
z
(
xz
)
y
when according to
the selection rules both transverse and longitudinal modes arise (
а
), at scattering
geometry
z
(
xz
)
x
when only transverse modes arise (
b
), at scattering geometry
x
(
zy
)
x
when only longitudinal modes arise (
c
)
38
ISSN 1812-3368. Herald of the BMSTU. Series “Natural Sciences”. 2015. No. 1